The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top to bottom within a group. SP 64 and the strength of its Coulombic interaction with water molecules.
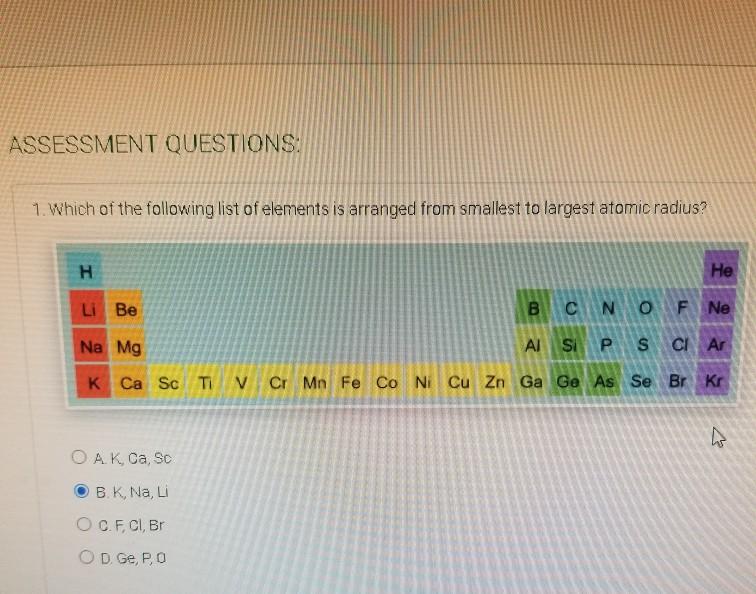
Solved Assessment Questions 1 Which Of The Following List Chegg Com
SAMPLE EXERCISE 73 Atomic and Ionic Radii Arrange Mg Ca2 and Ca in order of.

. B Ag Al Co Cr Fe and Zn form substitutional solid solutions of incomplete solubility. The atomic radius of Sc is 162 p m Ti is 147 p m F e is 126 p m and that of C o is 125 p m. The electronic configuration of F e is A r 3 d X 6 4 s X 2 and that of C o is A r 3 d X 7 4 s X 2.
726 Brown Using only the periodic table arrange each set of atoms in order of increasing radius. Al Be Si 728 Brown Explain the following variations in atomic or ionic radii. What is its atomic radius.
B Determine the atomic radius for Co in the equiatomic bcc FeCo alloy given that it has a lattice constant a 028571 nm. 97 rows For example the atomic-ionic radius of chlorine Cl- is larger than its atomic radius. As atomic increases with in a period the atomic radii decreases.
The atomic radius decreases across a period. Ca2 Mg2 Be2 Fe Fe2 Fe3 Explain the trend in cation and anion size compared to their neutral atom. The characteristic radius ranges from 30 to 200 pm.
The attic radii of Fe Co and Ni are approximately the same. What is its atomic radius. Students were asked in parts a through c to use principles of atomic structure to predict the electron configuration of Fe2 LO 119.
The closer you are to the nucleus the smaller the atomic radius. Determine the atomic volume for Fe in the bcc structure given that it has a lattice constant a - 028683nm. EXPLAIN WHY THE FOLLOWING IS TRUE.
Bookmark this question. Explain why the atomic radii of Helium and Neon are so close when considering Neon has 1 more energy level. Can anybody please explain to me the effect of difference in ionic and atomic radii of dopant and host material on crystallinity and other factors.
Comparing carbon C with an atomic number of 6 and fluorine F with an atomic number of 9 we can tell that based on atomic radius trends a carbon atom will have a larger radius than a fluorine atom since the three additional protons the fluorine has will pull its electrons closer to the nucleus and shrink the fluorines radius. And this is. The difference in atomic number and hence the difference in the number of 3d electrons is 1.
All these metals have either BCC or HCP crystal structures andor the difference between their atomic radii and that for Ni are greater than 15 andor have a valence different than 2. What is the general group trend for atomic radius. The atomic radius of a chemical element is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell of an electron.
SP 64 and explain differences in its ionic radius LO 119. State and explain qualitatively the variations in atomic radius and ionic radius across a period and down a group. Increasing in size moving across and decreasing moving down the periodic table.
C C H and O form interstitial solid solutions. Sn - Sb stays the same Sb - Te increases. However its tricky to measure the ionic radius not the least because charged atomic ions repel each other.
B Ag Al Co Cr Fe and Zn form substitutional solid solutions of incomplete solubility. Helium smallest 31 pm Cesium largest 265 pm What happens to atomic radii within a period as the atomic number increases. Atomic Radius of all the elements in the Periodic Table in Graph and Table format Complete information about all the properties of elements using Graphs and Tables Interactive Dynamic Periodic Table Periodic Table Element Comparison Element Property trends and complete information about the element - Facts How to Locate on Periodic Table History Abundance.
A Determine the atomic volume for Fe in the bcc structure given that it has a lattice constant a 028683 nm. The atomic radius of Iron atom is 132pm covalent radius. Experimental observations and atomicmolecularbulk structure.
Depending on the definition the term may apply only to isolated atoms or also to atoms in condensed matter covalently bound in. Explain the differences in the atomic radii for Fe and Co. The anion ionic radius is the same as or slightly larger than the atomic radius.
We have synthesized undoped and Fe doped La2O3. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus. Actual order of atomic radius of this series is.
Therefore atomic size decreases from left to right along the period in 3d series but there is exception for this series. The ionic radius is the radius of an atom forming an ionic bond or an ion. This is the order.
C C H and O form interstitial solid solutions. Show activity on this post. All these metals have either BCC or HCP crystal structures andor the difference between their atomic radii and that for Ni are greater than 15 andor have a valence different than 2.
Overall the trend for the ionic radius is the same as for the atomic radius. The bond length between atoms A and B is the sum of the atomic radii d AB r A r B. This is because the number of protons and therefore the.
The measuring unit for the ionic radius is Armstrong A 0 or picometers pm. I- I I. Slater JC 1964 Journal of Chemical Physics 393199-Crystal Radii.
Cite any exceptions to the vernalization you stated in your answer to the question above. What makes the sodium atom different from the magnesium atom. As in 3d series atomic number increases from left to right hence effective nuclear charge increases.
The atomic bonds restrict the electrons and nucleus and due to this the ions or atoms dont have a specific shape. Determine the atomic radius for Co in the equiatomic bcc FeCo alloy given that it has a lattice constant a 028571nm. C Explain the differences in the atomic radii for Fe and Co.
CrystalMaker uses Atomic-Ionic radii data from. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physical entity there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius. Does anyone knowcan explain the differences between Neutral atomic radii after Clementi et al 19631967 and the empirically measured covalent radii from Salter al 1964.
In other words as the principal quantum number of the outermost occupied or of an ion increases the radius of the ion increases. The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. Up to 256 cash back For ions carrying the same charge ionic radius increases as we move down a column in the periodic table Figure 77.
Crystal Structure FCC Element Ni Atomic Radius nm 01246 Electronegativity 18 Valence 0071 H 0046 0060 01445 01431 01253 01249 FCC 14 15 17 16 1 Ag Al Co FCC HCP BCC 3 2 3 Cr Fe Pt Zn 01241 01387 ВСС FCC 17 15 2 2 01332 HCP 17 2 Which of these elements would you expect to form the following with nickel. It must be noted atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary.
Atomic Radius Trend Periodic Table Chemtalk
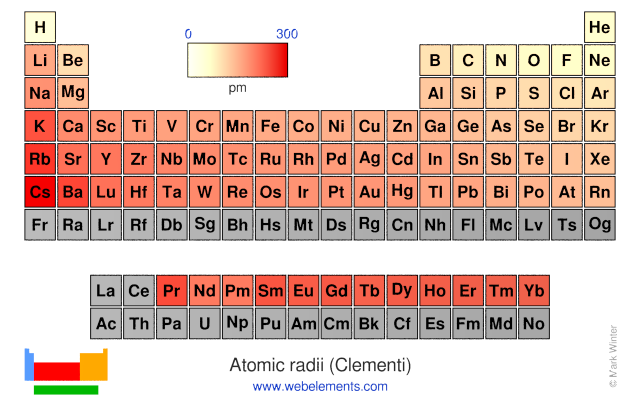
Webelements Periodic Table Periodicity Atomic Radii Clementi Periodic Table Gallery
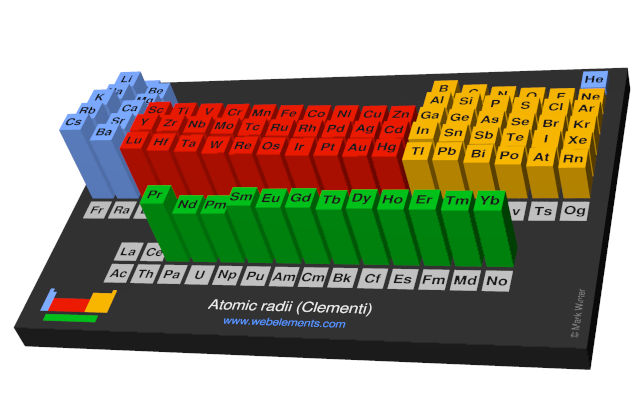
Webelements Periodic Table Periodicity Atomic Radii Clementi Periodic Table Gallery
0 Comments